Review of lead-acid battery separators
In the traditional flooded lead-acid battery, the separator only acts as an inert spacer to prevent the short circuit of the positive and negative electrodes. It needs to have good ionic conductivity, the manufacturing method is matched with the production process, the physical and chemical properties have long-term stability, etc.
In valve-regulated lead-acid batteries (VRLA), in addition to the above properties, the separator also needs to Has the following properties:
(1) As electrolyte storage, the separator must be able to absorb enough electrolyte to ensure the discharge capacity of the battery, and at the same time must have an appropriate porosity to ensure that the gas can be recombined;
(2) The separator must have sufficient resistance Tensile and mechanical strength to meet the needs of mechanized production;
(3) The separator must be insoluble in acid solution. And the impurity content should be small to prevent impurities from dissolving into the electrolyte and affecting the battery performance;
(4) The separator needs to have a high porosity, so that the acid liquid is evenly distributed, and the acid liquid flows smoothly during acid filling and formation;
(5) The separator needs to have a certain elasticity to ensure that the separator is always in a tight state with the electrode plate during the charging and discharging cycle of the battery;
(6) The separator must be able to absorb enough electrolyte, and at the same time ensure that the battery is in a state of poor liquid;
(7) The separator must allow the electrolyte to flow freely in it, especially to provide a gas path for oxygen circulation and recombination when the battery is in an overcharged state.
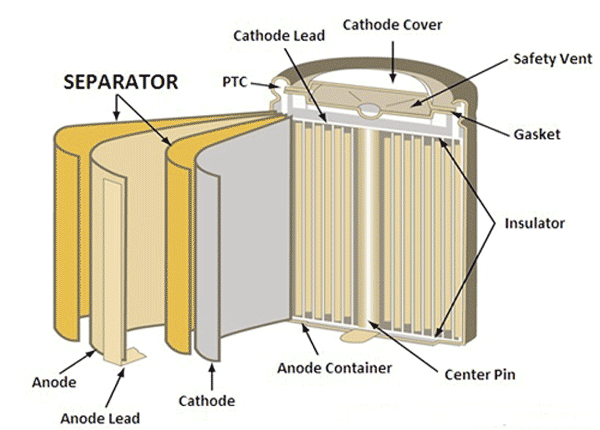
Different types of lead-acid batteries require separators:
Start the ignition lighting battery. This type of battery must generate a large instantaneous current when working. Therefore, the battery performance of the separator is very high. Considering all aspects, the following requirements are put forward for the battery: small resistance to facilitate high current discharge; small resistance. Acid discharge to facilitate battery capacity; small pore size to prevent lead dendrites from penetrating the separator; high strength to facilitate battery assembly.
Industrial lead-acid batteries
Valve-regulated sealed lead-acid batteries can be used for emergency lights, UPS, telecommunications, radio and television, railways and navigation marks, etc. This type of battery needs a small current to discharge continuously, and it puts forward higher requirements for the separator: it can quickly absorb electrolyte , and the electrolyte retention ability is strong; small pore size and high porosity; can maintain elasticity under dry and wet conditions, so that the plate always maintains a certain positive pressure; when the separator is saturated with liquid, there is still a gas passage to Conducive to oxygen circulation and recombination, to achieve uniform thickness of battery sealing. Error is small.
Lead-acid batteries for tractionare mainly used for traction energy of locomotives, golf carts, electric forklifts and automatic guided vehicles. The requirements for the separator are as follows: have excellent mechanical strength, prevent damage caused by vibration, friction and compression during handling and assembly, and prevent the separator from being pierced; have good flexibility, suitable for assembly line assembly; small aperture to prevent Penetration of dendrites; good oxidation resistance. Prevents separators from softening and cracking during battery operation; excellent heat resistance (lead-acid batteries for traction sometimes operate at 75°C).
