Take you to understand the VRLAB
The working principle of VRLAB can be summarized as follows:
The positive electrode plate undergoes water decomposition reaction, which causes O2 precipitation and generates H+ ions.
O2 and H+ ions diffuse to the negative electrode plate through the gas channel and the liquid channel in the separator.
After reaching the negative electrode plate, oxygen reacts with H+ ions to generate water.
The generated water is diffused to the positive electrode plate through the separator, so that the water electrolyzed by the positive electrode plate is recovered.
The above reaction forms the so-called closed oxygen cycle (COC). The closed oxygen cycle significantly reduces the battery's water loss during charging and overcharging, making it maintenance-free.
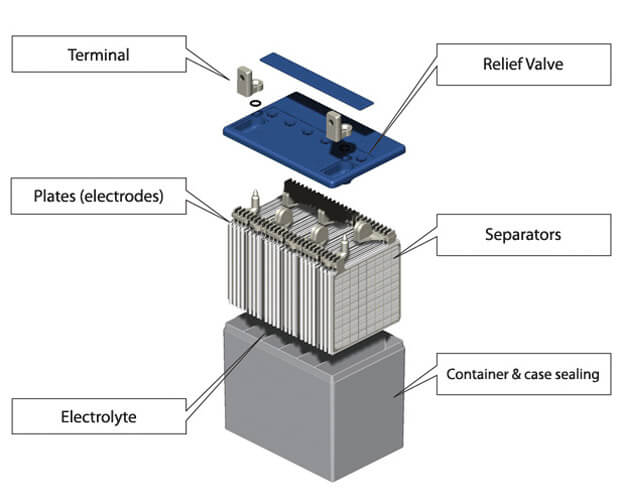
Depending on the separator type and electrolyte state, the two basic technologies employed in VRLA batteries are:
(1) Batteries using adsorbed glass fiber mat (AGM batteries), the electrolyte of which is adsorbed in the AGM separator. Adsorbent glass fiber contains no more than 85% glass fiber with a length of 1~2mm, and contains 15% polymer fiber (polyethylene, polyphenylene, etc.) as a reinforcing material. Glass fibers are hydrophilic, and their function is to adsorb electrolyte, while polymer fibers provide mechanical support and also have a certain degree of hydrophilicity, which can promote the formation of gas channels.
When the VRLA battery was put into use, 95% of the AGM micropores were filled with electrolyte, and the remaining 5% of the micropores formed gas channels for oxygen to flow between the two plates. With the extension of the cycle time, the battery loses water, and the electrolyte saturation of the AGM separator decreases to 90%, then to 85%, and so on. Subsequently, COC efficiency increased. However, this is related to the thermal problem and eventually leads to capacity attenuation.
(2) Batteries using colloidal electrolyte (Gel batteries), the electrolyte of this battery is a non-flowing thixotropic colloid, which contains SiO2 and Al2O3 particles with a diameter of several nanometers. Use the same polymer separator used in flooded batteries to separate the positive and negative plates. Gel batteries, like flooded batteries (which contain a flowing electrolyte), also lose water when they start to use. As a result, the colloid shrinks and cracks form inside. These cracks form oxygen channels. The oxygen evolved from the positive plate reaches the negative plate, so that the COC starts to operate and the water loss stops. The operating mechanism of the COCs of all types of VRLA batteries is the same, regardless of the type of separator used (same as AGM or gel separator, search agm separator, CLICK HERE).
Each cell of the VRLA battery has a pressure reducing valve (instead of the vent cap of the flooded battery), which can maintain a certain gas pressure above the battery pole group consisting of the electrode plate and the separator. The oxygen reduction reaction occurs in the negative plate, which greatly reduces the oxygen pressure at the negative plate in the pole group. In this way, a diffusion gradient is formed inside the pole group, which guides the oxygen flow to the negative plate. Therefore, the pressure relief valve is an essential part of VRLAB.
